Paediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fracture
Supracondylar Fracture
Patient Presentation
Age 6-10 years
MOI - Fall on outstretched hand with elbow on extension, breaks. Olecranon serves as the fulcrum and the stress concentrates in distal humerus. Anteriorly the perisoteum hinges.
Pain , swelling, deformity, bruising
Deformity (usually S shaped ) , skin puckering
Compartment syndrome
Blood vessels spasm/ contusion/ tear/ thrombosis
If capillary refill present , hand arm Dunlop traction done.
No role of Angiography , further delays the treatment.
Nerve Injuries, proximal fragment spike hits nerve.
3a Posteromedial displacement - Radial Nerve involvement
3b Posterolateral displacement - Median Nerve involvement
Gartland and Wilkins Classification
Extension type fracture
1. Undisplaced Fracture
2. Displaced Fracture , posterior cortex is. intact
3. Displaced fracture, posterior cortex breaks
Flexion type occur with direct injury on elbow on flexed position.
95 % are extension type of fracture.
X-ray - AP image shows level of fracture, displacement . Lateral image helps classifying flextion or extension type. Fat pad sign is important.
Management
Type I - Slab or Long Arm Cast
Type II - Slab or LAC
Medial column communition requires pinning
Type III - Pinning or Open Reduction and fixation
Reduction
Realign coronal tilt
Push anteriorly to correct extension
Open Reduction Indications
Failure of closed methods
NV compromise
Open fractures
Pinning
Cross pinning - Most stable
Lateral - Divergent most stable
Convergent - less stable
Parallel - least stable, tuggling
Wilkins recommend 2 Divergent pins from lateral side , one pin high in shaft is gives the most stable construct. (Proponent of lateral pin entry )
Assessment of Reduction
Anterior humeral line touches capitellum
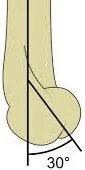
Metaphyseal Diaphyseal angle < 40 degrees
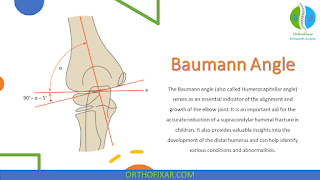
Correction of Baumann's angle
Anterior Humeral Line
https://radiopaedia.org/articles/anterior-humeral-line
Common Complications
Pin Migration
Infection
Cubitus Varus
Cubitus Valgus
Recurvatum
Nerve Palsy
Vascular Injury
Volkmann Ischaemic Contracture
Post-operative Stiffness
Please give your comments , if I missed anything and how can I improve.
Also Check
https://orthonp.blogspot.com/2020/04/algorithm-3-for-management-of-fracture.html



Comments
Post a Comment