Cervical Spine Dislocation
C5 displacement over C6 , (displacement > 50 % , it's a Bifacet dislocation )
Delayed Diagnosis of B/l facet dislocation :a case report.Julie O Shaughnessy et. al.
Only shows C7 and is inadequate for trauma C-spine lateral radiograph.
Management
- ATLS guideline -remove helmet visor to gain access to eyes , nose and mouth.
- Exclude other injuries.
- Full imaging of spine / full neurological examination - ensure this is isolated injury.
- Spine surgery consultation for reduction
Close or Open
- Exclude a prolapsed disc which damages cord during reduction.
If no MRI scanner, can we reduce with patient awake ?
Yes, we can reduce. We can monitor patient awake, alert .Serial neurological examination is also possible.
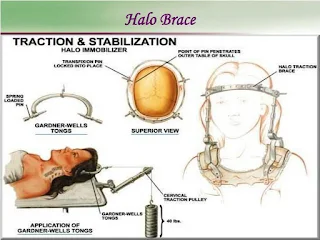
Gardner-Wells-Tong / Crutchfield skull traction is applied on skull and then adding sequential weights to traction cord.
Patient positioned on supine, under C-arm guidance, after each addition of weight load, image taken and assessed. Initially 10 pounds then 5 pounds added. Once neck is fully stretched, facets unlocked then neck is fully extended to complete the reduction and traction reduced.
How do we apply a Halo traction Jacket?
Take the consent.
Four pins using local anaesthesia applied on skull, tightened with a torque limiter (6 pins for children)
Placement carried out as follows -
1. Anterior - 1 cm above lateral outer 1/3rd of eyebrow
2. Posterior - Behind earlobe above mastoid
Three Person Job- one holding head and two applying Halo.
Apply Jacket of approximate size.
Check radiograph of spine to ensure correct reduction.
Tighten pins after 24 hours.
https://www.slideserve.com/taber/critical- care-of-spinal-cord-injury-dr-amr-el-said- professor-of-anaesthesia-intensive-care- faculty- of-medicine.
Complications
Loss of reduction
Pin site infection and Loosening
Pain
Nerve Injury




Comments
Post a Comment