Management of Open Shaft of Tibial Fracture
Open Fractures of Tibia Diaphysis
(Daniel N. Segina, Robert V. Cantus, David Templeman )
How do you manage such a case ?
ATLS review. R/o life threatening and more urgent issues.
Examine wound, photograph it, cover it with a saline soaked gauze.
Analgesia
Splinting
Antibiotics
Tetanus Toxoid
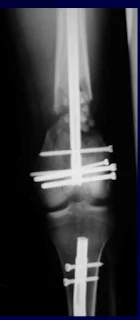
Obtain AP and Lateral radigraphs
transfer to theatre
Initial wash /scrub for gross contamination
Thorough debridement of skin, fat, fascia, muscle, bone
Fracture stabilization before further wash out.
Dressing, splint leg with physical examination
make a plan for further management.
continue ex-fixator or remove the ex-fixator , back slab and convert to IMIL after few. weeks when pin tracts heal
What is the biggest concern post-operatively ?
With high energy trauma, particularly tibial fractures may lead to compartment. syndrome.
Regular observations
Invasive procedure for those who have a reduced level of consciousness
Techniques of fasciotomy
Two incision technique - advised by British Orthopaedic Association
Ist long incision- medial to postero- medial border of tibia, allows posterior compartment decompression
2nd Incision- 2 cm lateral to anterior border of tibia
- access to anterior. border of tibia
- access to anterior and lateral compartment
How soon to get soft tissue to cover ? recommendation - within 5 days of initial injury
soft tissue coverage based on reconstruction ladder.
most complex - free flap
involves taking a distant muscle with its. vascular supply and revascularizing it. with a healthy vessel close to recipient site.
Please give feedback if you have any in comment section.




Comments
Post a Comment