Discussion Supracondylar Fracture of Distal Humerus
Age 6- 10 years
common in boys.
Fall on outstretched hand (FOOSH) - common mechanism of injury.
Break in periosteum anteriorly , hinge force posteriorly.
Extension fracture in 95 % of cases
Flexion type fracture in 5 % of cases .
Extension type fracture classification of Gartland and Wilkin's
1. Undisplaced fracture
2.Displaced fractures , posterior cortex intact
3.Displaced fracture , posterior cortex breaks
Flexion type
direct injury on elbow on flexed position.
Patient presentation
1. history of trauma
2.pain , swelling , deformity , bruises on arm
3.Deformity - S-shaped , puckering ,
4.compratment syndrome
( It may be due to vessel spasm , contusion , tear , thrombosis
If capillary refill present , hand arm Dunlop traction given. )
5.Nerve injuries
proximal fragment spike hits the nerve.
type 3a posteromedial displacement - radial nerve injured
type 3b with posterolateral displacement - ulnar nerve affected.
flexion type injury results in Ulnar nerve injury
X-ray description
AP film
s/c fracture , fracture line oblique or transverse through olecranon fossa
displaced or undisplaced
Lateral - fracture displacedment direction , fat pad signs
Tr.
1.Type I - Slab / LAC
2. Type II - Slab / LAC
Medial column communition - pinning
3. Pinning /Open
Reduction - realign coronal tilt
push anteriorly to correct extension .
X-ray assessment
Lateral Landmarks
posterior margins of coronid fossa
anterior margins of olecranon fossa
Shaft condylar angle
angulation of 40 degrees between the long axis of humerus and long axis of lateral condyle
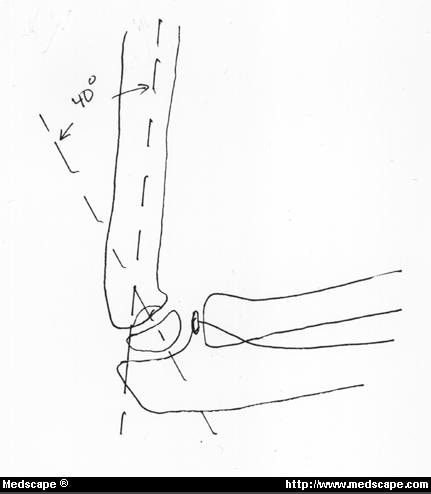
Humeral ulnar angle - best resembles the carrying angle of elbow .
AP Film
Bauman's angle - 64 to 81 degrees

https://www.google.com/search?q=baumans+angle+in+supracondylar+fracture+royalty+free+images&tbm=isch&ved=2ahUKEwib7rWjlPzoAhXZFHIKHVqEA8MQ2-cCegQIABAA&oq=baumans+angle+in+supracondylar+fracture+royalty+free+images&gs_lcp=CgNpbWcQA1C55xhY3-8YYIj3GGgAcAB4AIABuQSIAfUPkgEHMi02LjUtMZgBAKABAaoBC2d3cy13aXotaW1n&sclient=img&ei=KkmgXpuxIdmpyAPaiI6YDA
Open reduction indications
failure of closed methods
NV compromise
open fractures
Pining Types
Most stable - Cross Pinning
Lateral - Divergent
Convergent - less stable
parallel - least stable , toggles
Wilkin's Recommendation. - 2 divergent pins from lateral side ; of them one pin high in shaft leads to most stable fixaiton . He is a proponent of lateral pin entry.
common in boys.
Fall on outstretched hand (FOOSH) - common mechanism of injury.
Break in periosteum anteriorly , hinge force posteriorly.
Extension fracture in 95 % of cases
Flexion type fracture in 5 % of cases .
Extension type fracture classification of Gartland and Wilkin's
1. Undisplaced fracture
2.Displaced fractures , posterior cortex intact
3.Displaced fracture , posterior cortex breaks
Flexion type
direct injury on elbow on flexed position.
Patient presentation
1. history of trauma
2.pain , swelling , deformity , bruises on arm
3.Deformity - S-shaped , puckering ,
4.compratment syndrome
( It may be due to vessel spasm , contusion , tear , thrombosis
If capillary refill present , hand arm Dunlop traction given. )
5.Nerve injuries
proximal fragment spike hits the nerve.
type 3a posteromedial displacement - radial nerve injured
type 3b with posterolateral displacement - ulnar nerve affected.
flexion type injury results in Ulnar nerve injury
X-ray description
AP film
s/c fracture , fracture line oblique or transverse through olecranon fossa
displaced or undisplaced
Lateral - fracture displacedment direction , fat pad signs
Tr.
1.Type I - Slab / LAC
2. Type II - Slab / LAC
Medial column communition - pinning
3. Pinning /Open
Reduction - realign coronal tilt
push anteriorly to correct extension .
X-ray assessment
Lateral Landmarks
posterior margins of coronid fossa
anterior margins of olecranon fossa
Shaft condylar angle
angulation of 40 degrees between the long axis of humerus and long axis of lateral condyle

Humeral ulnar angle - best resembles the carrying angle of elbow .
AP Film
Bauman's angle - 64 to 81 degrees
https://www.google.com/search?q=baumans+angle+in+supracondylar+fracture+royalty+free+images&tbm=isch&ved=2ahUKEwib7rWjlPzoAhXZFHIKHVqEA8MQ2-cCegQIABAA&oq=baumans+angle+in+supracondylar+fracture+royalty+free+images&gs_lcp=CgNpbWcQA1C55xhY3-8YYIj3GGgAcAB4AIABuQSIAfUPkgEHMi02LjUtMZgBAKABAaoBC2d3cy13aXotaW1n&sclient=img&ei=KkmgXpuxIdmpyAPaiI6YDA
Open reduction indications
failure of closed methods
NV compromise
open fractures
Pining Types
Most stable - Cross Pinning
Lateral - Divergent
Convergent - less stable
parallel - least stable , toggles
Wilkin's Recommendation. - 2 divergent pins from lateral side ; of them one pin high in shaft leads to most stable fixaiton . He is a proponent of lateral pin entry.



Comments
Post a Comment